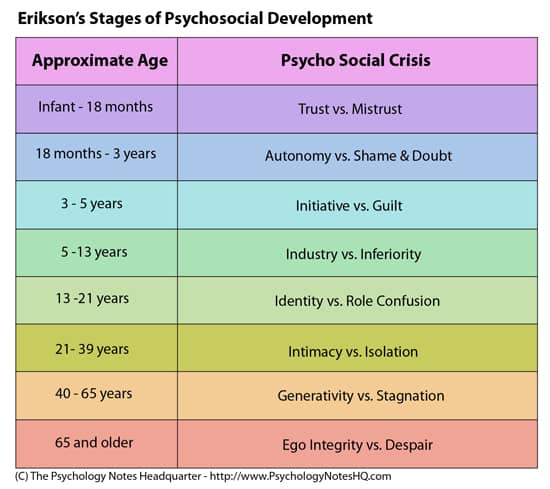
Question 9

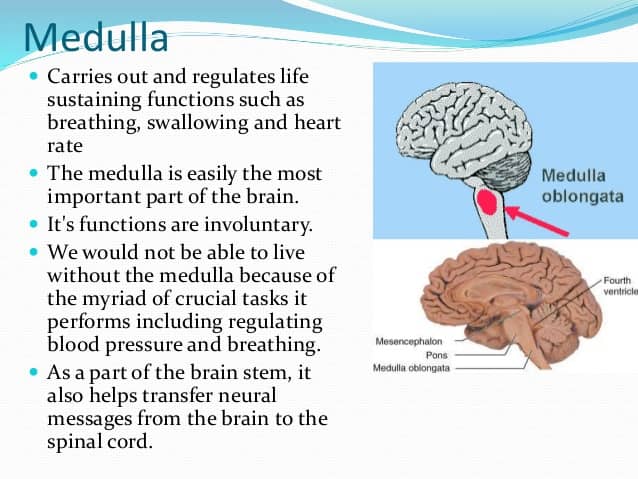
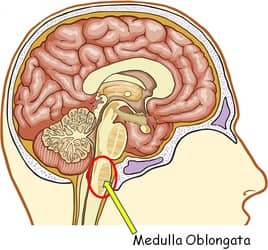
- Carries out and regulates life sustaining functions such as breathing, swallowing and heart rate
- It's functions are involuntary, or done without thought.
Question 11

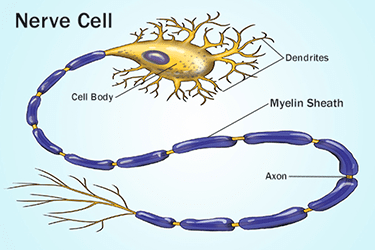
- The main purpose of myelin is to increase the speed at which electrical impulses propagate along the myelinated fiber
- In unmyelinated fibers, electrical impulses (action potentials) travel as continuous waves, but, in myelinated fibers, they "hop" or propagate by saltatory conduction.
Question 12

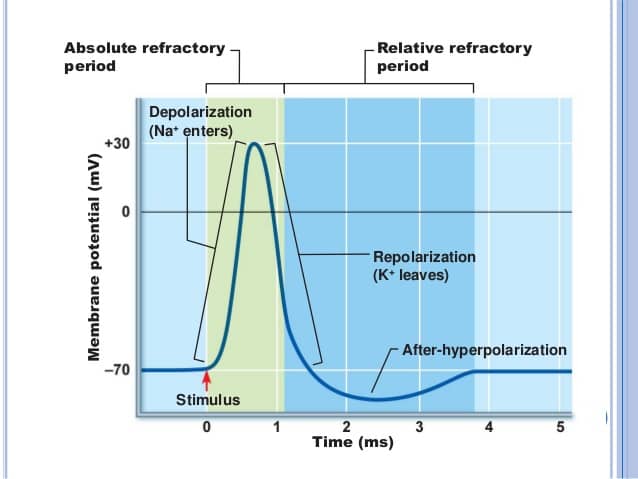

Question 13

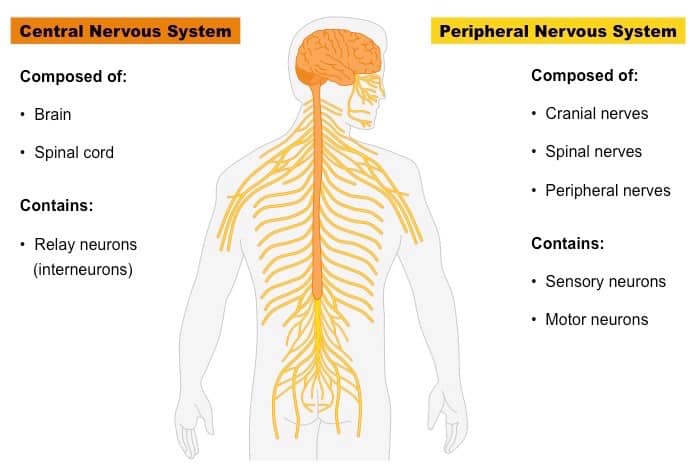
Question 14

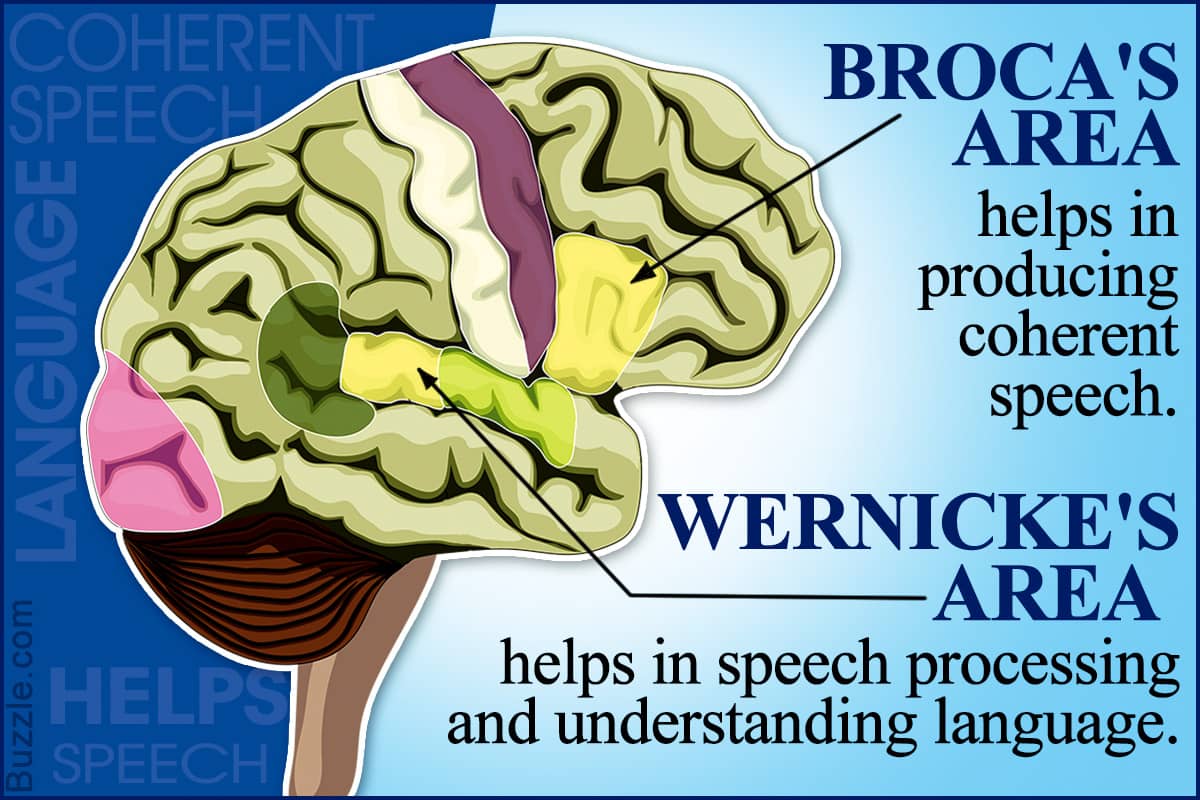
Question 15

- Adrenaline: a hormone secreted by the adrenal glands, especially in conditions of stress, increasing rates of blood circulation, breathing, and carbohydrate metabolism and preparing muscles for exertion.
- Steroid: any of a large class of organic compounds with a characteristic molecular structure containing four rings of carbon atoms
- Acetylcholine: a compound that occurs throughout the nervous system, in which it functions as a neurotransmitter
- Endorphin: The principal function of endorphins is to inhibit the communication of pain signals; they may also produce a feeling of euphoria very similar to that produced by other opioids
- GABA: a neurotransmitter that blocks impulses between nerve cells in the brain
Question 16

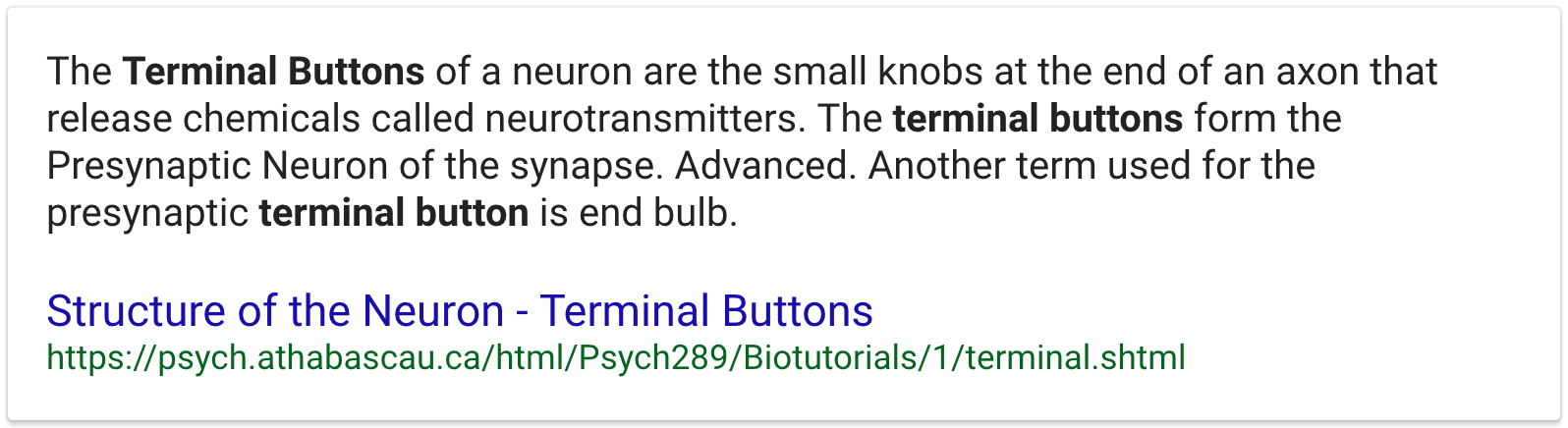
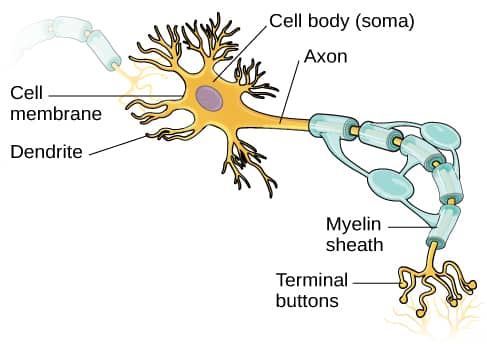
Question 17

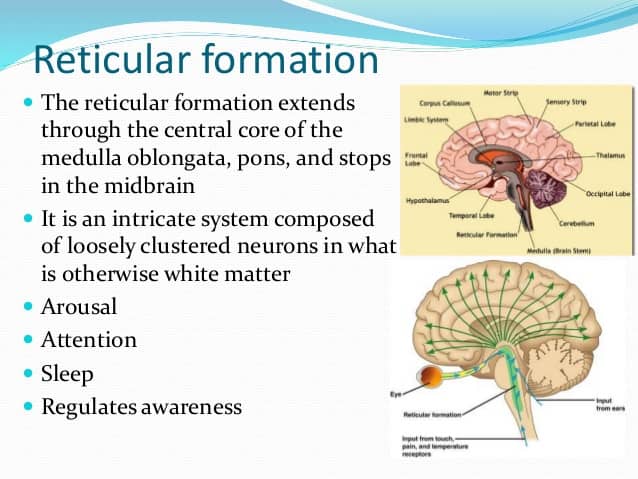
Question 18

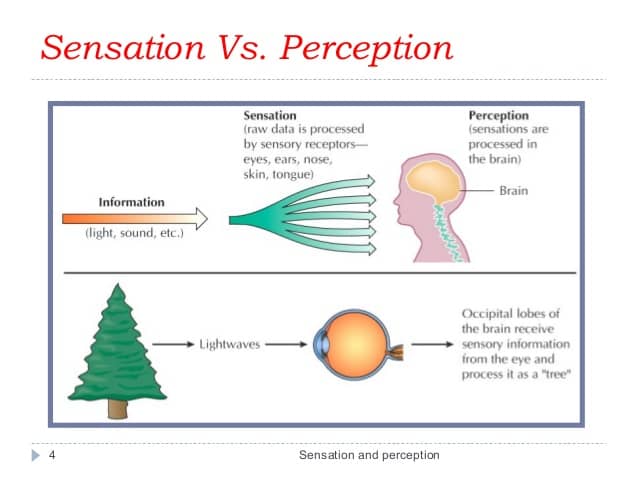
Question 20

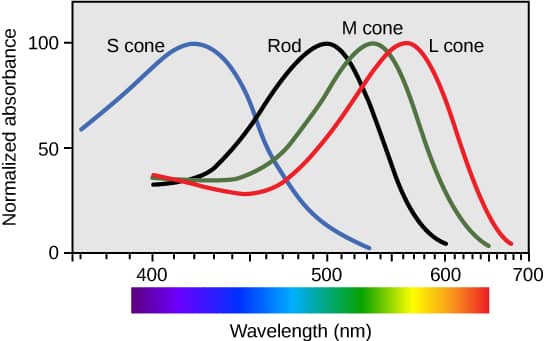
Sensory adaptation
a change over time in the responsiveness of the sensory system to a constant stimulus.

Weber's Law
the change in a stimulus that will be just noticeable is a constant ratio of the original stimulus.

The Young–Helmholtz theory
a theory of trichromatic color vision – the manner in which the photoreceptor cells in the eyes of humans and other primates work to enable color vision.
Opponent-process theory
- a psychological and neurological model that accounts for a wide range of behaviors, including color vision
Opponent process theory suggests that color perception is controlled by the activity of two opponent systems: a blue-yellow mechanism and a red-green mechanism.
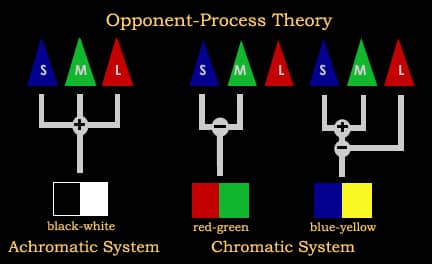
Feature detection theory
- The nervous system sorts or filters complex natural stimuli in order to extract behaviorally relevant cues that have a high probability of being associated with important objects or organisms in their environment, as opposed to irrelevant background or noise.
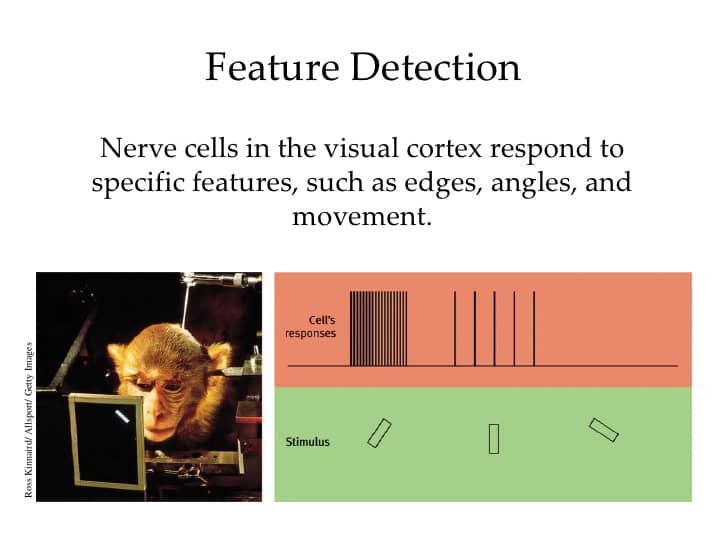
- The nervous system sorts or filters complex natural stimuli in order to extract behaviorally relevant cues that have a high probability of being associated with important objects or organisms in their environment, as opposed to irrelevant background or noise.
Question 21

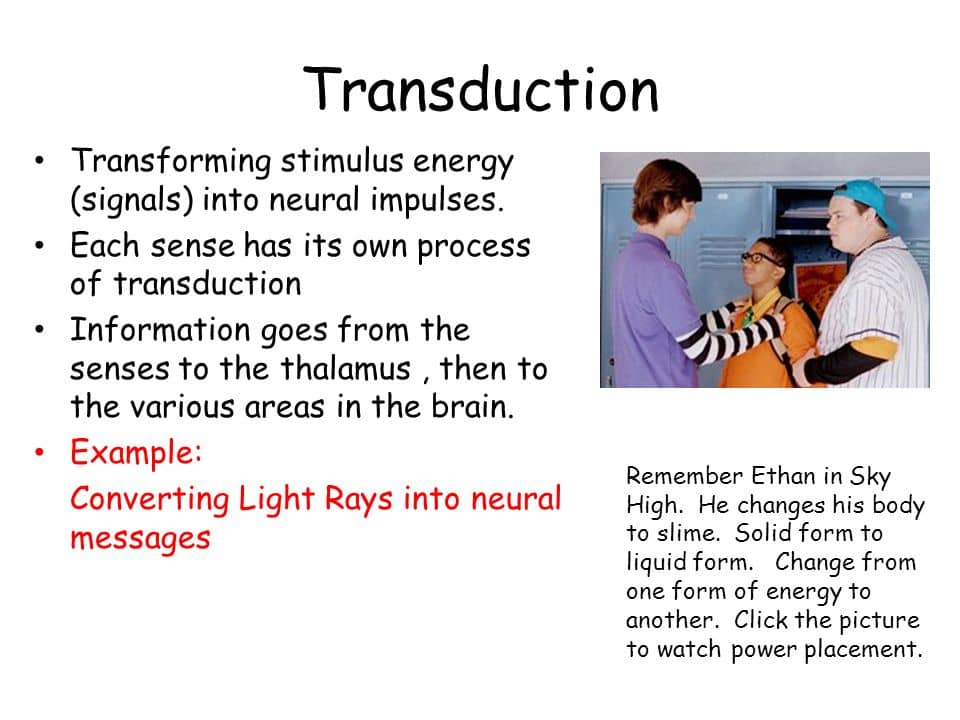
Question 22
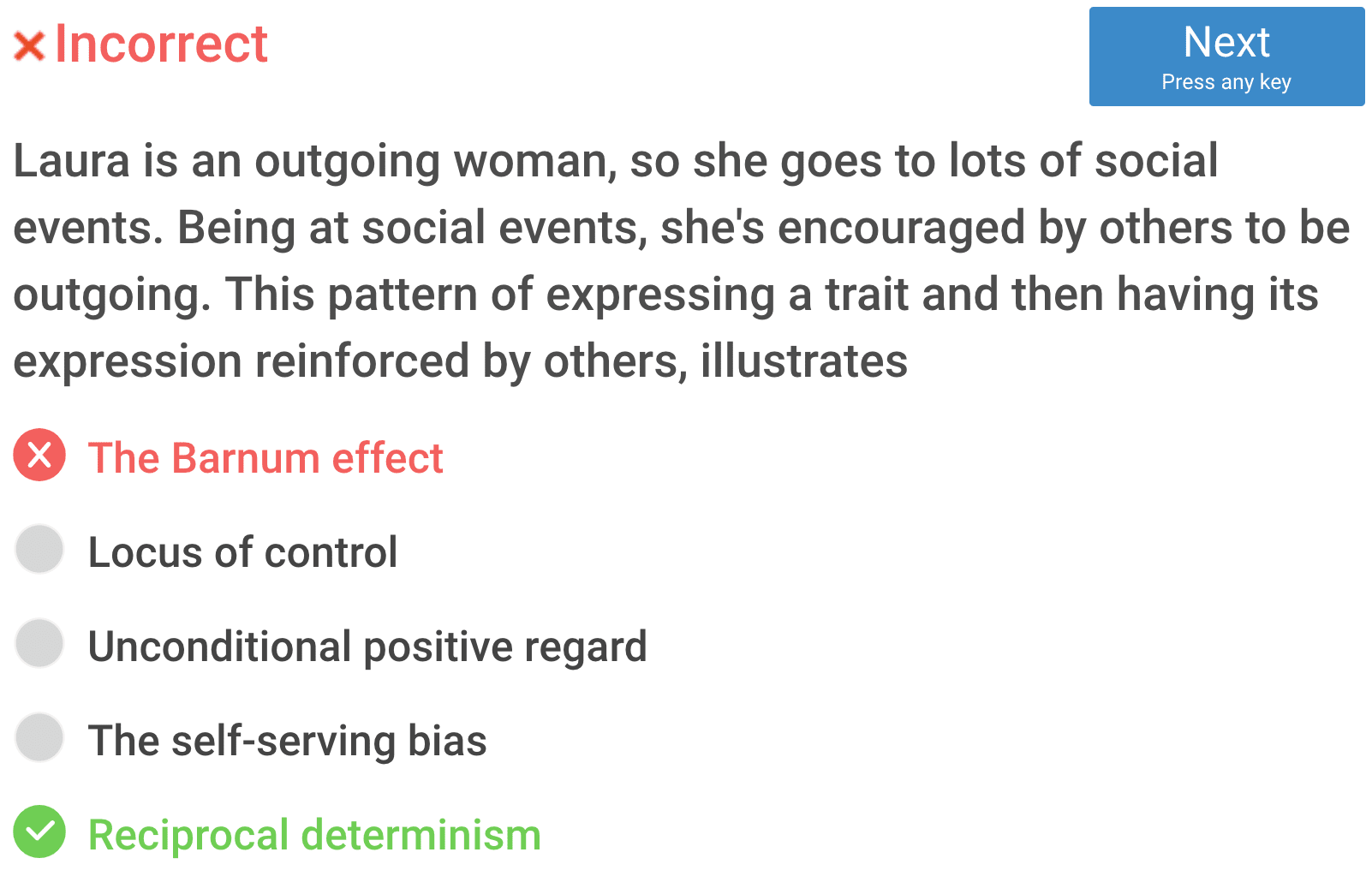
The Barnum effect
a common psychological phenomenon whereby individuals give high accuracy ratings to descriptions of their personality that supposedly are tailored specifically to them, that are in fact vague and general enough to apply to a wide range of people


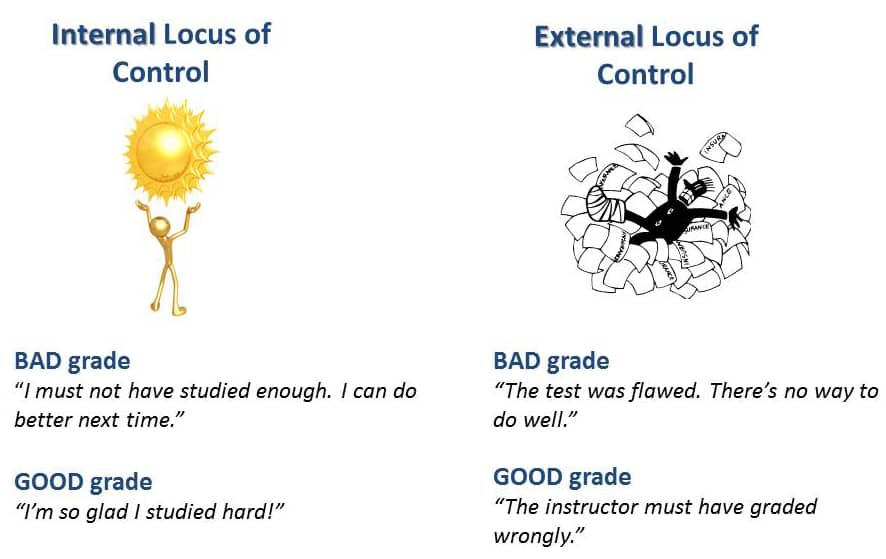
Locus of control
A person with an internal locus of control believes that he or she can influence events and their outcomes, while someone with an external locus of control blames outside forces for everything.
The self-serving bias
A self-serving bias is any cognitive or perceptual process that is distorted by the need to maintain and enhance self-esteem, or the tendency to perceive oneself in an overly favorable manner.

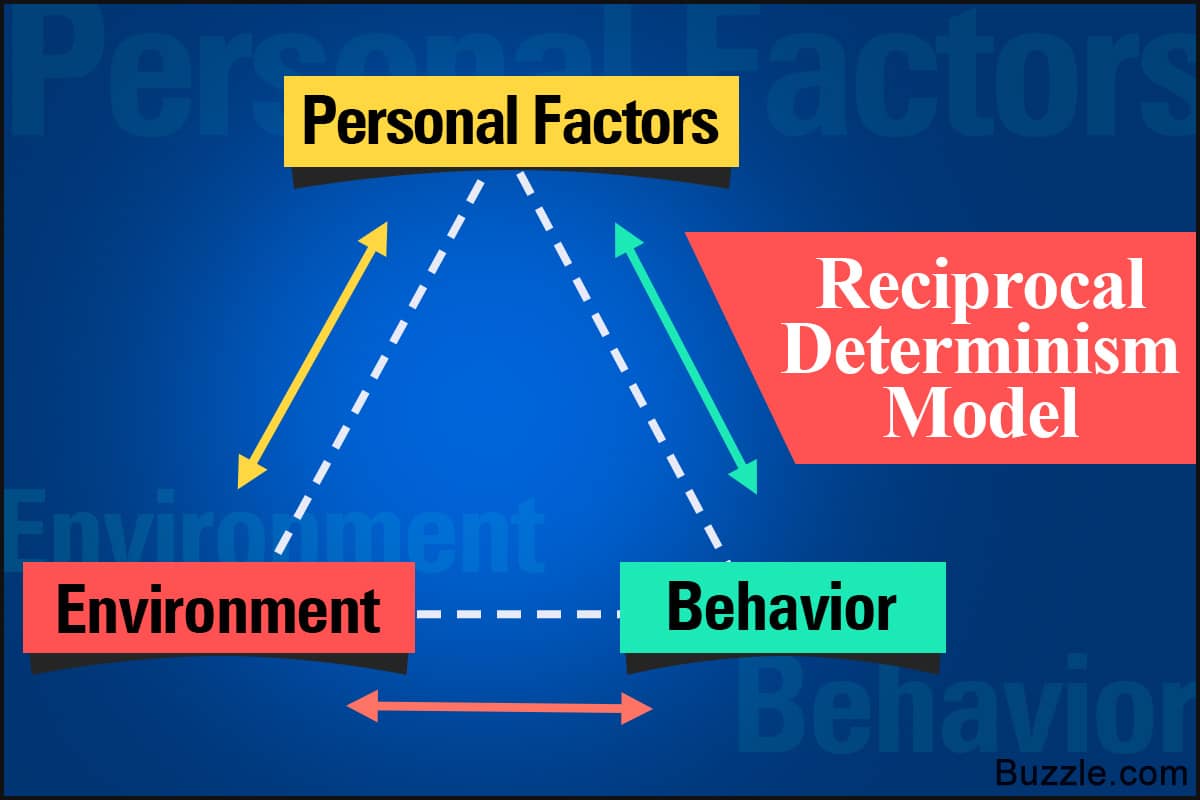
Reciprocal determinism
a person's behavior both influences and is influenced by personal factors and the social environment
Question 23

- Dissociative Identity Disorder = Multiple Personality Disorder
Question 25

Question 26

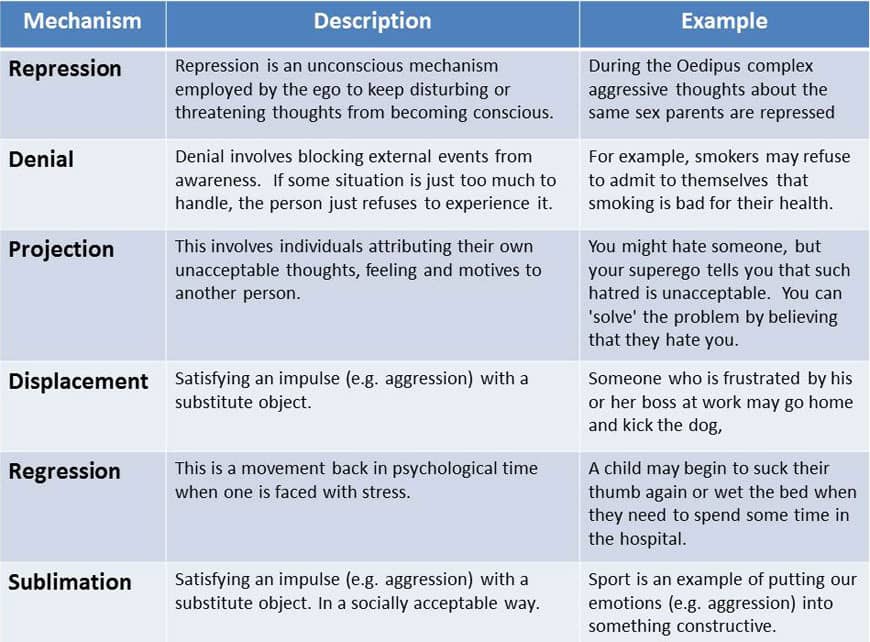
Question 27

- Generalized anxiety disorder (or GAD) is characterized by excessive, exaggerated anxiety and worry about everyday life events with no obvious reasons for worry.
Question 28

- Zygote: a diploid cell resulting from the fusion of two haploid gametes; a fertilized ovum.
- Embryo: the early developmental stage of an animal while it is in the egg or within the uterus of the mother
- Fetus: an unborn offspring of a mammal, in particular an unborn human baby more than eight weeks after conception
Question 32
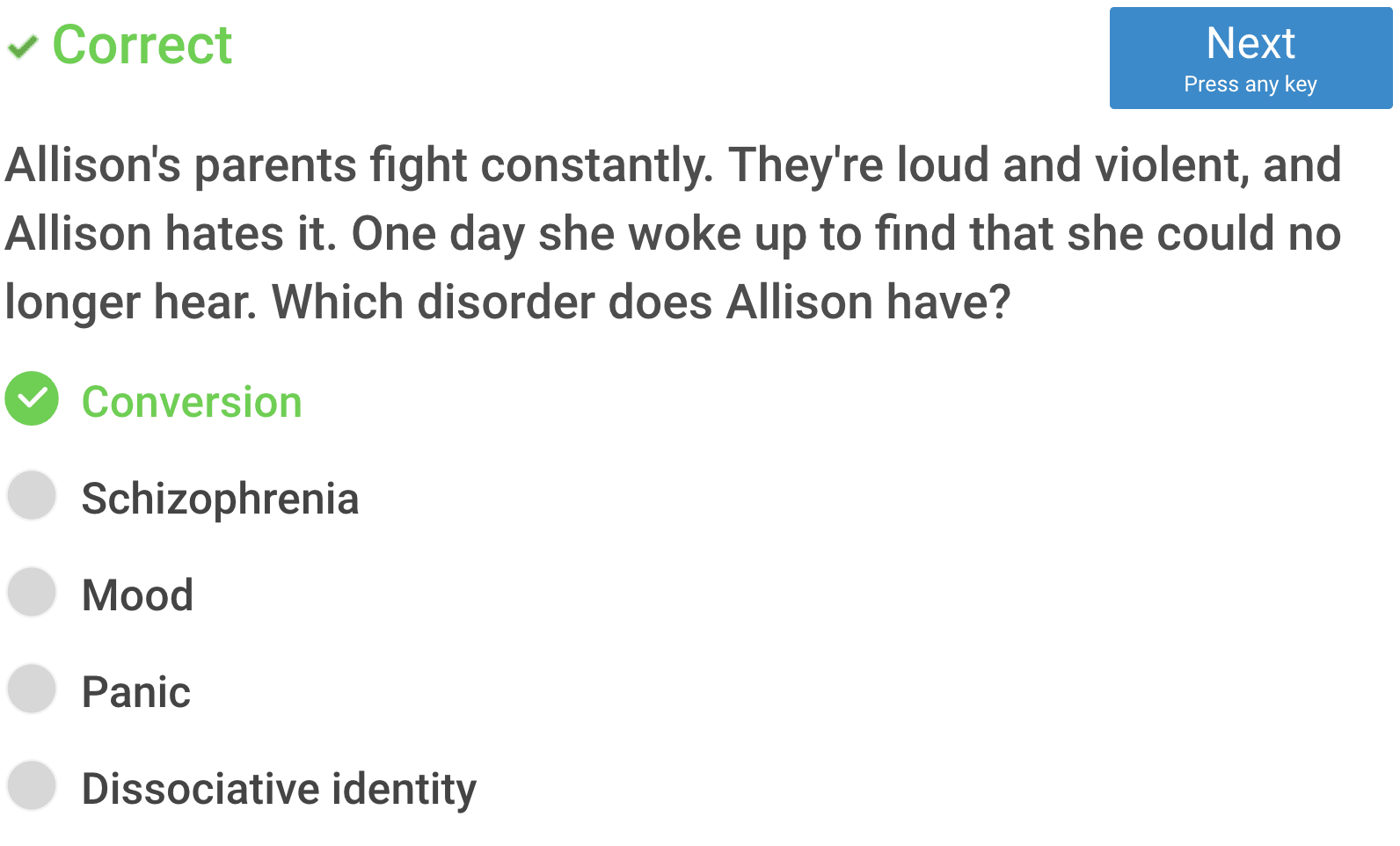
Conversion disorder is a mental condition in which a person has blindness, paralysis, or other nervous system (neurologic) symptoms that cannot be explained by medical evaluation.

Question 34


Question 38

Question 40

- Thorazine is used to manage and reduce hallucinations, delusions, extreme emotions, and other related symptoms that generally accompany schizophrenia

Question 41

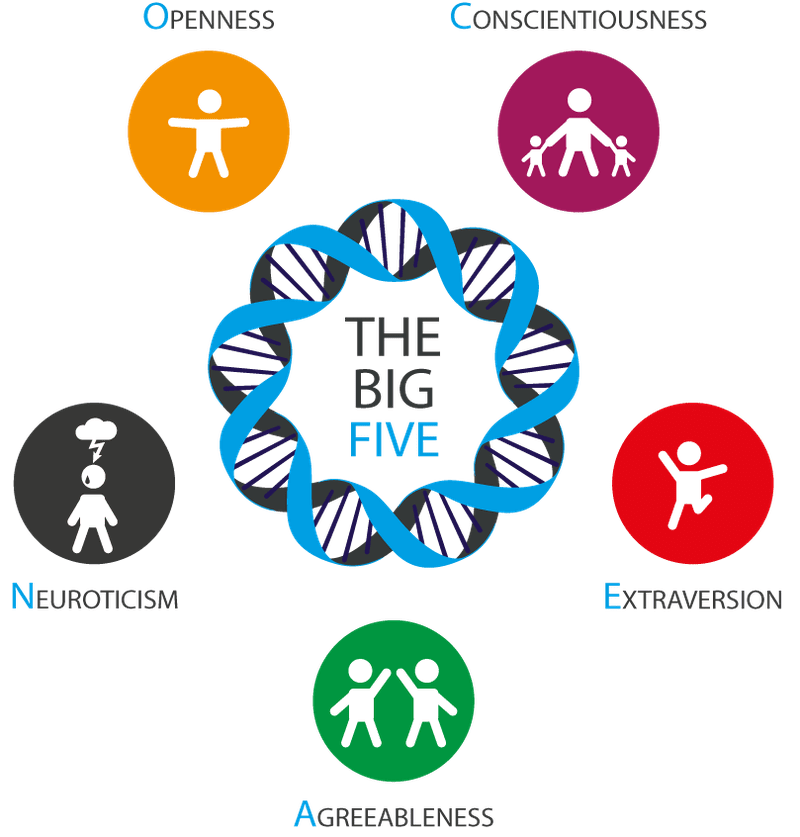
Question 45

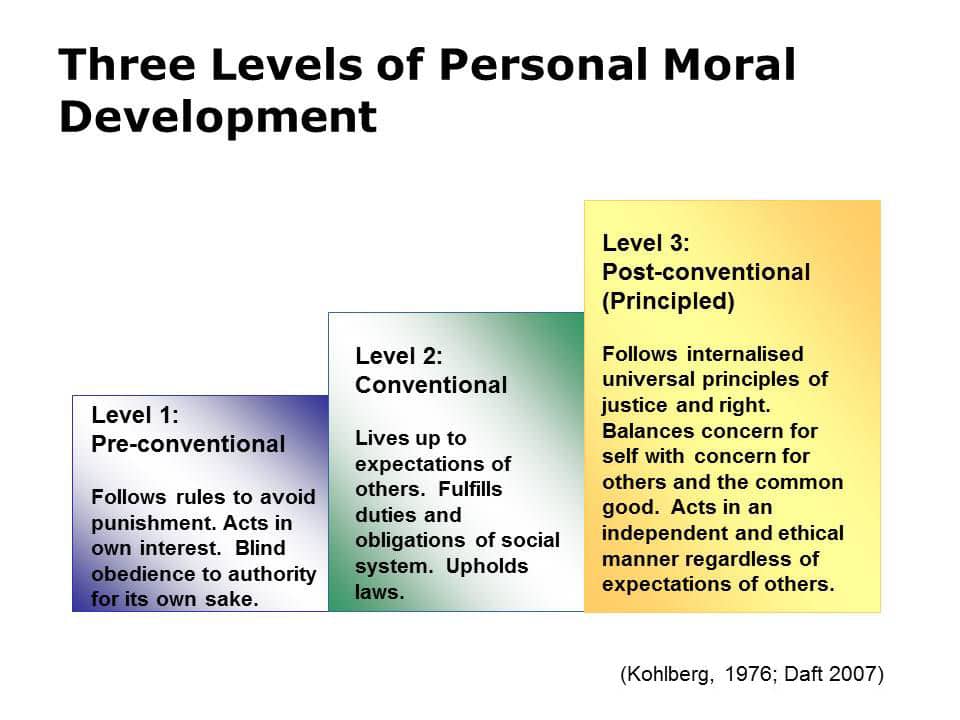
Question 51

Question 55

Question 57
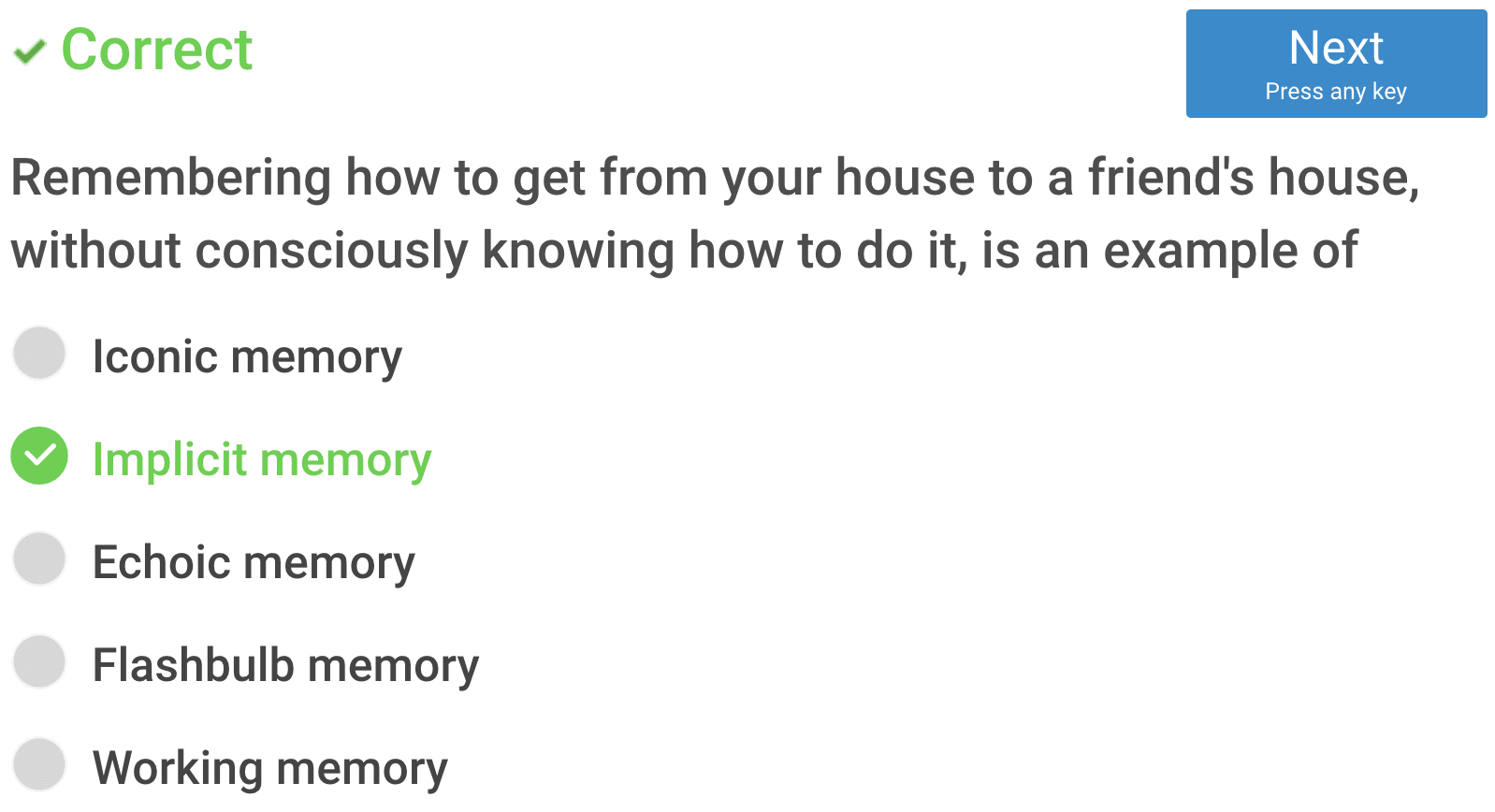
- Iconic memory is part of the visual memory system which also includes long-term memory and visual short-term memory. It is a type of sensory memory that lasts very briefly before quickly fading.
- Implicit memory is one of the two main types of long-term human memory. It is acquired and used unconsciously, and can affect thoughts and behaviours.
- Echoic memory is the sensory memory register specific to auditory information (sounds).
- A flashbulb memory is a highly detailed, exceptionally vivid 'snapshot' of the moment and circumstances in which a piece of surprising and consequential (or emotionally arousing) news was heard.
- Working memory is a cognitive system with a limited capacity that is responsible for temporarily holding information available for processing
Question 60

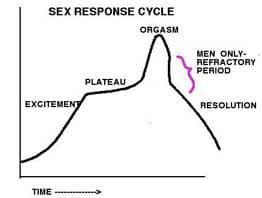
Question 61


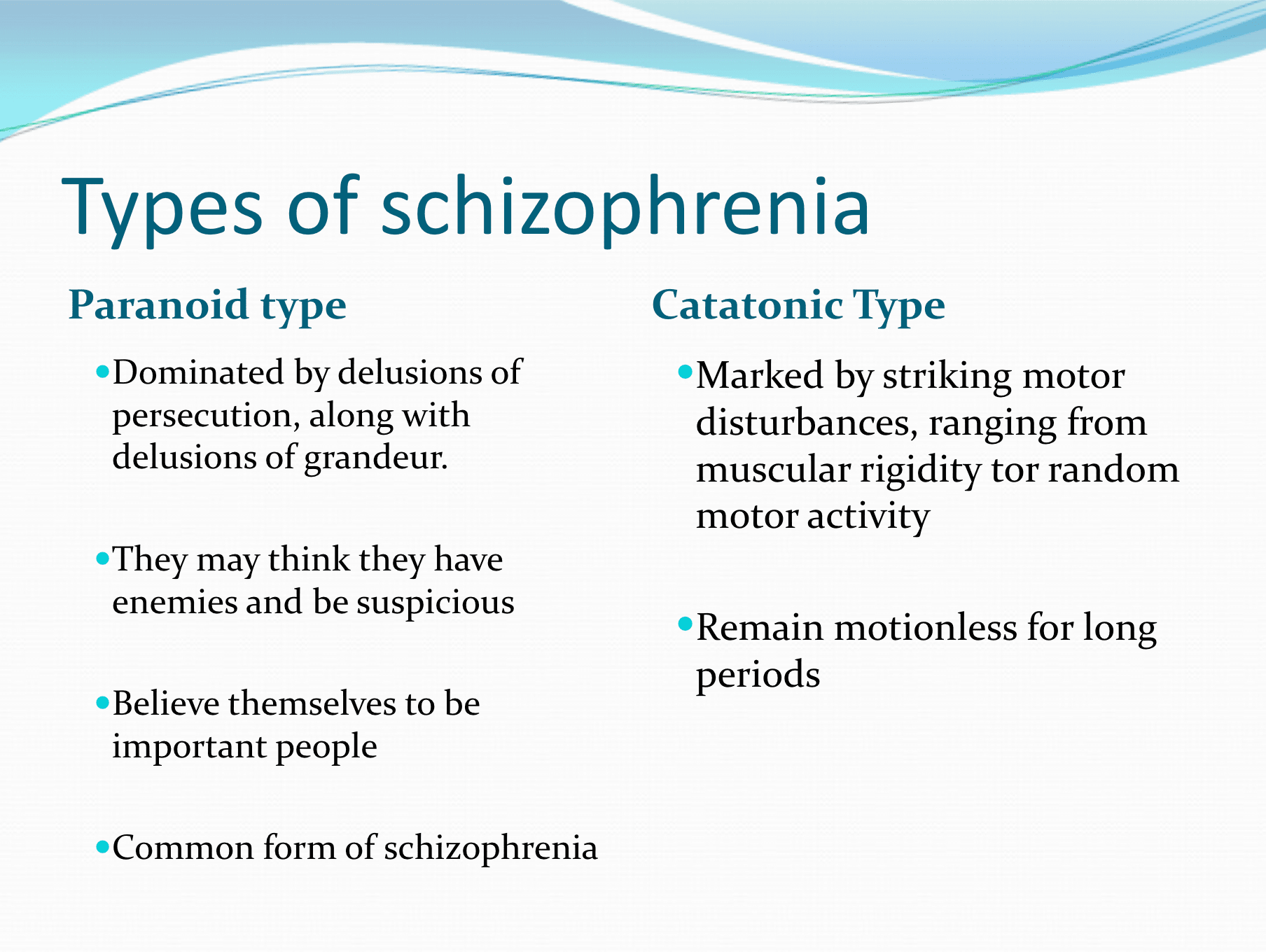
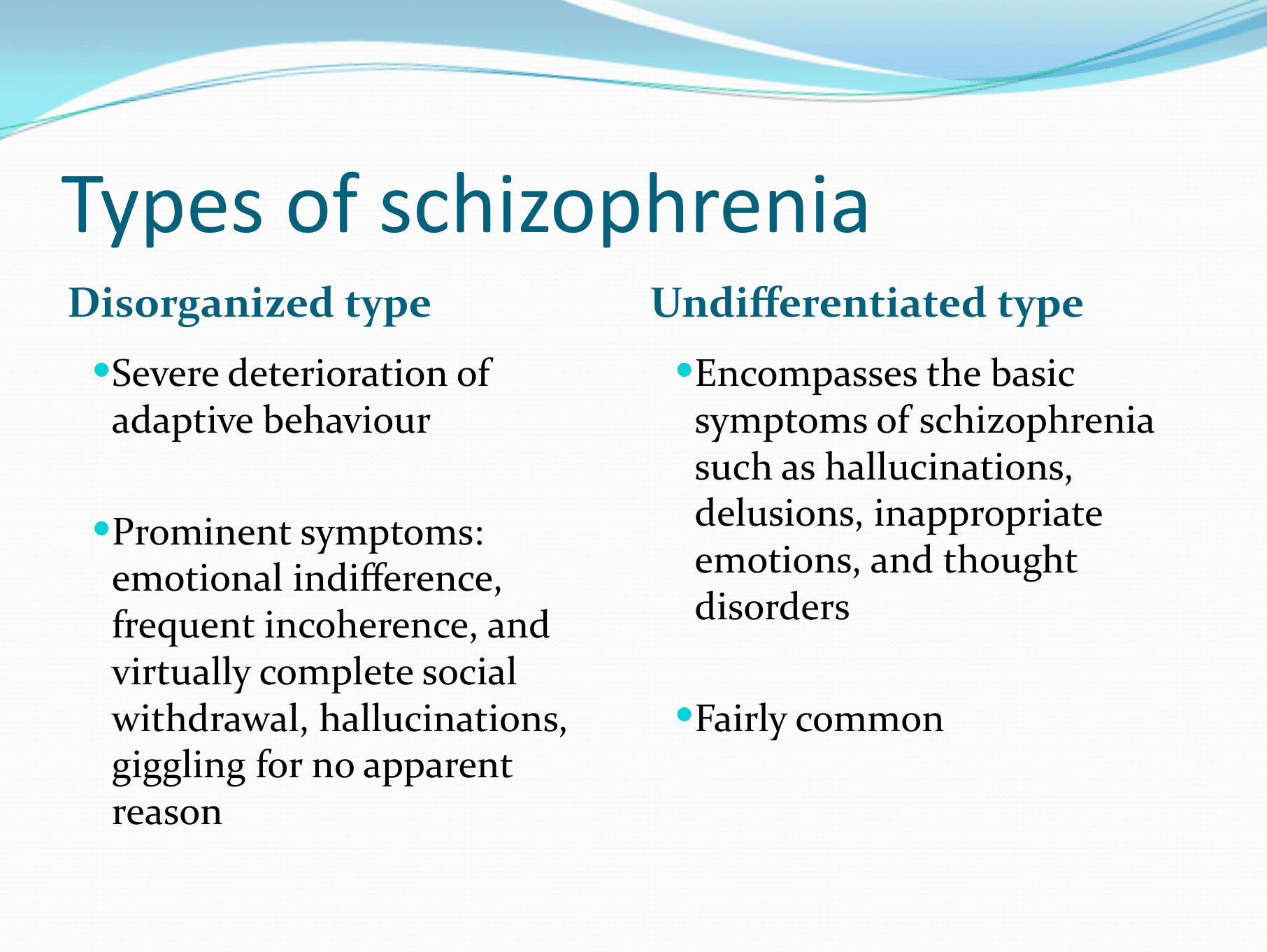
Question 64

Question 66

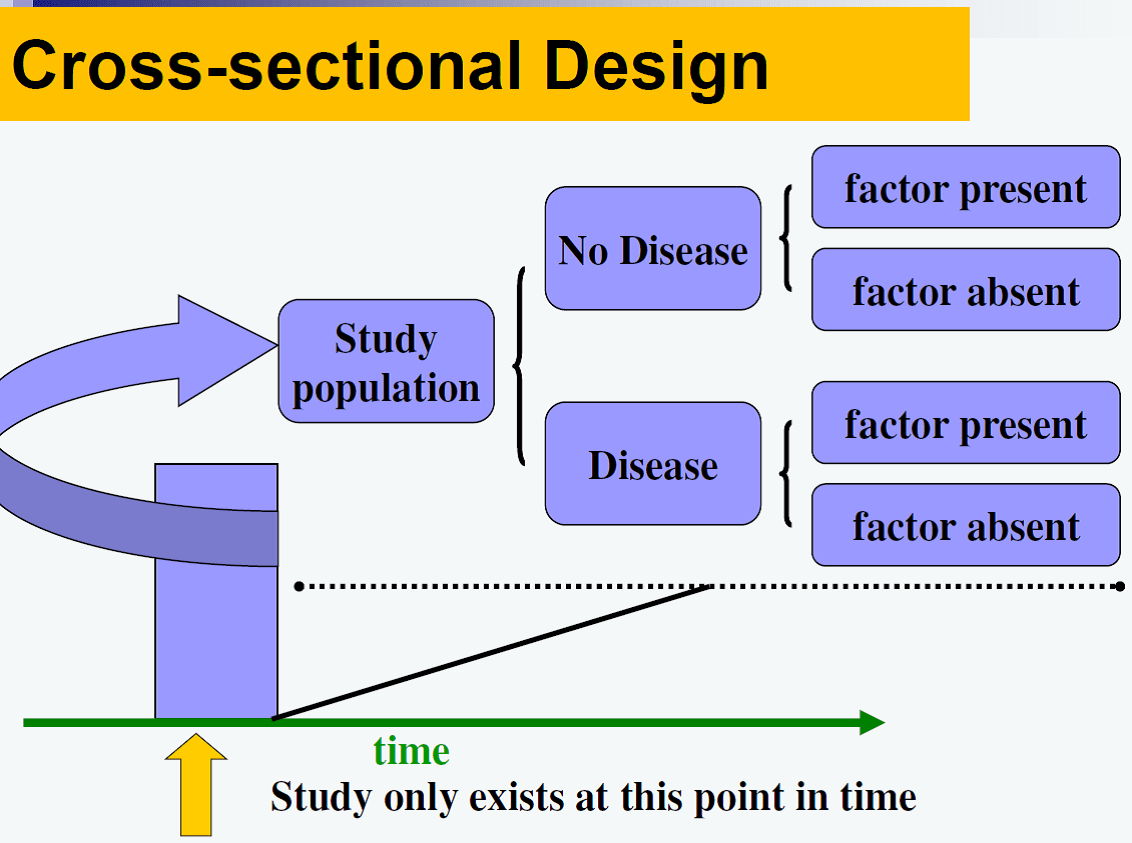
Question 70


Question 72

- Emotional attachment/bonding is the deep, enduring emotional connection between ourselves and specific people that we know and that are important to us.
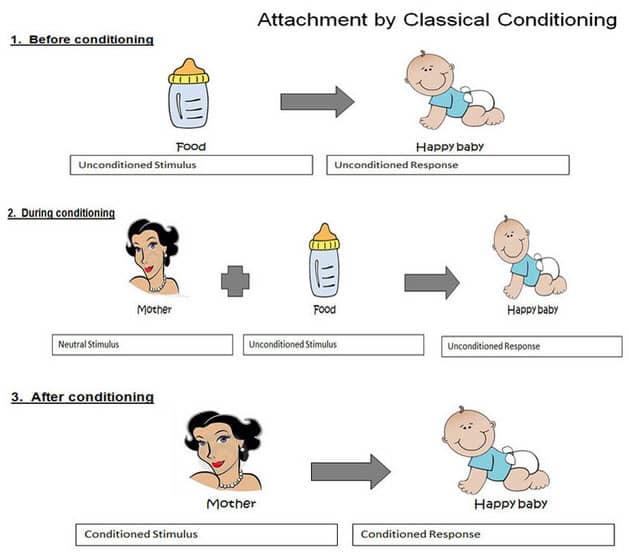

Question 73

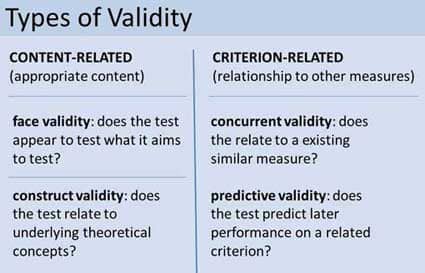
- Face validity: the degree to which a procedure, especially a psychological test or assessment, appears effective in terms of its stated aims.
- Predictive validity: the extent to which a score on a scale or test predicts scores on some criterion measure
- Content validity: how well an instrument (i.e. a test or questionnaire) measures a theoretical construct
- Construct validity: the degree to which a test measures what it claims, or purports, to be measuring
Question 74

Question 78


Qusetion 79

Question 82

- In psychology, heuristics are simple, efficient rules which people often use to form judgments and make decisions.
- They are mental shortcuts that usually involve focusing on one aspect of a complex problem and ignoring others.
Question 85
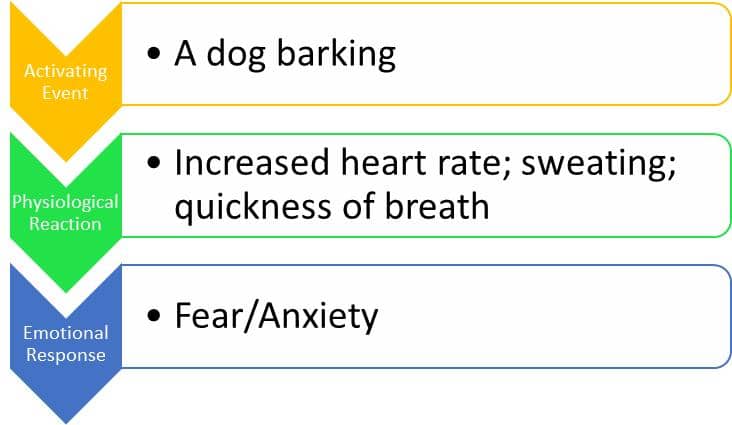
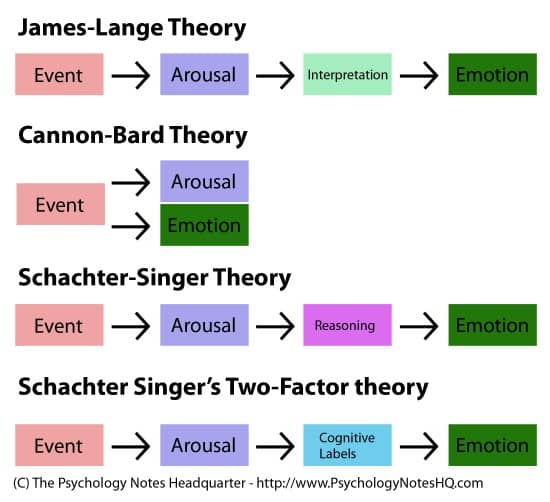
Question 87

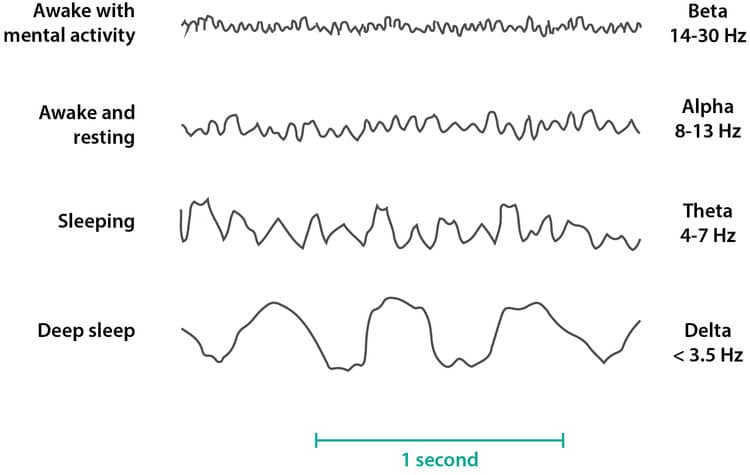
Question 90

Question 92

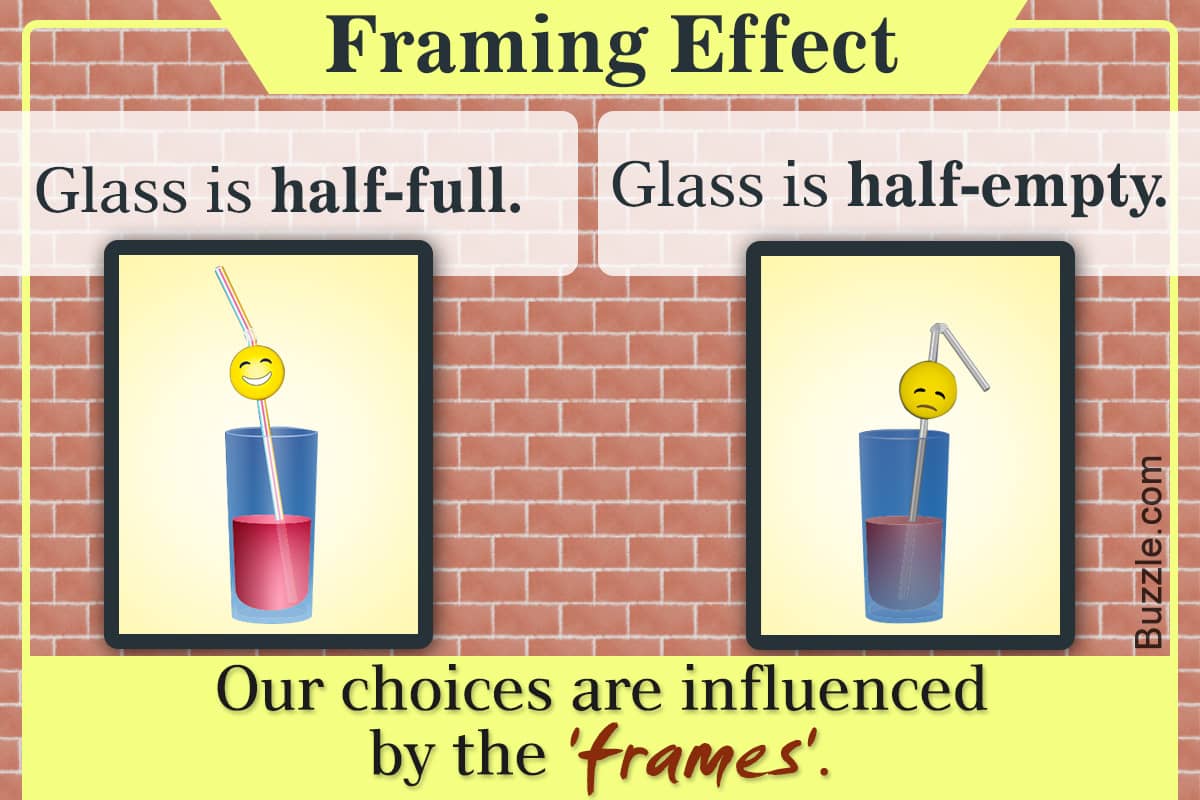
The framing effect
The framing effect is an example of cognitive bias, in which people react to a particular choice in different ways depending on how it is presented
Belief perseverance
Belief perseverance, also known as belief persistence, is the inability of people to change their own belief even upon receiving new information or facts that contradict or refute that belief.

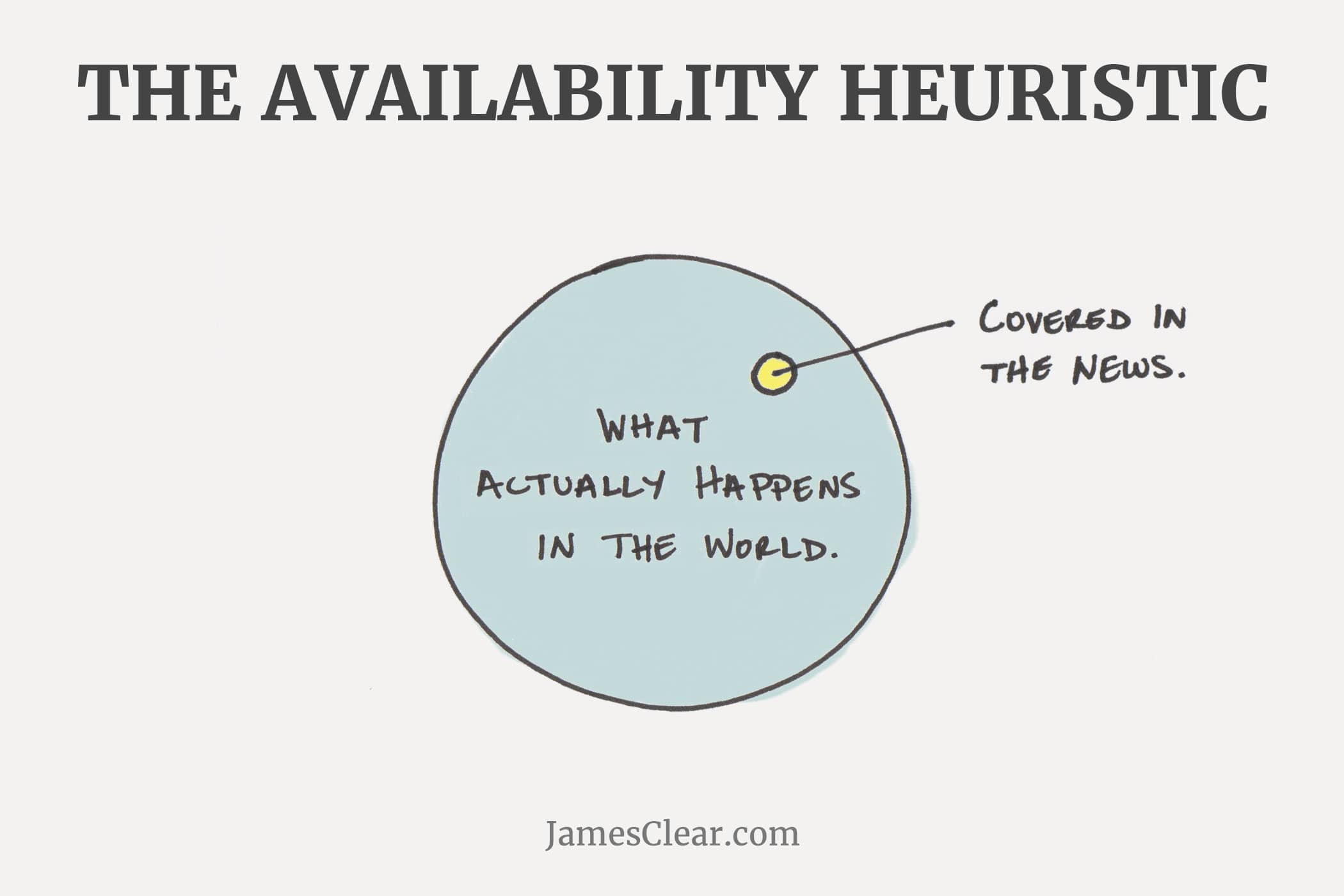
Availability heuristic
The availability heuristic is a mental shortcut that relies on immediate examples that come to a given person's mind when evaluating a specific topic, concept, method or decision.
Representative heuristic
The representativeness heuristic is used when making judgments about the probability of an event under uncertainty

Question 93